Danger rhombus

The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) has developed a standard called NFPA 704 that is used to identify hazards of materials (especially chemicals).
Among occupational health and safety experts, this standard is known as the Hazard Diamond. It seems that the rescue diamond would be a more appropriate name for the hazard diamond!
This diamond itself is made up of 4 other diamonds, each of which has a different color, and each color has a specific meaning.
The meaning of the colors in the hazard diamond:
- Health Hazards Blue color identifies health hazards
- Flammability Hazards Red color identifies flammability hazards
- Reactivity Hazards Yellow color identifies reactivity hazards
- Specific Hazards White color identifies specific hazards
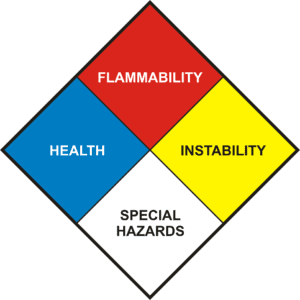
Inside these colored diamonds, there are numbers, the larger the numbers, the higher the level of danger.
So let's remember: the larger the numbers in the danger diamond, the higher the level of danger.
Number of danger level
4 | Extreme |
3 | Serious |
2 | Moderate |
1 | Slight |
0 | Minimal |
In short, we can say: The hazard diamond gives us general information about the dangers of chemicals.
The meaning of the numbers in combination with the colors in the hazard diamond:
HEALTH
4-Maximum
A highly toxic substance that has one or more of the following characteristics receives the number 4 in the blue part of the diamond:
- It causes death or serious injuries in very short exposures, requiring immediate medical attention.
- A substance that is carcinogenic, mutagenic or has the ability to affect the human fetus, which is definitely proven or suspected to cause these effects in humans. Examples: phosphine and hydrogen cyanide
3-Serious
A toxic substance that has one or more of the following characteristics receives the number 3 in the blue part of the diamond:
- It causes temporary or permanent injuries in short-term contact with humans, requiring immediate medical attention.
- A substance suspected of being carcinogenic in small animals or mutagenic or having the potential to affect the fetus in small animals. Example: Chlorine gas
2-Moderate
Moderately toxic substances that have one or both of the following characteristics are assigned a 2 in the blue part of the diamond:
Exposure to high concentrations of the chemical or prolonged exposure to it causes incapacitation (damage) or permanent damage unless prompt medical treatment is given.
Example: Ethyl ether
1- Mild
Lowly toxic substances that have one or more of the following characteristics are assigned a 1 in the blue part of the diamond:
May cause irritation or mild permanent damage that does not require special treatment.
Example: Acetone
0-Least
Known harmless substances that do not pose a health hazard are assigned a 0 in the blue part of the diamond:
Example: Lanolin
Flammability
4- Maximum
Materials that are highly flammable. Have a flash point below 23C or 73F.
Example: Propane
3-Serious
Flammable substances that have one or more of the following characteristics:
- Evaporate rapidly and can ignite (ignite) at almost any temperature
- May form explosive mixtures with air or burn rapidly in air
- May burn spontaneously and provide its own oxygen
- Have a flash point between (23C(73F) and (38C(100F).
Example: Gasoline
2-Moderate
Combustible materials that have one or more of the following characteristics:
- Must be exposed to high temperatures to ignite. (Acute)
- Must be heated to a uniform temperature to ignite. (Chronic)
- Solid materials that readily produce flammable vapors.
- Flash point between (8C(100F) and (93C(200F).
Example: Diesel fuel
1-Slight
Materials that are slightly flammable and have one or more of the following characteristics:
- When preheated to ignite
- Burn in air when exposed to (15.5C(1500F) for 5 minutes.
- Flash point not lower than (93.4C(200F).
Example: Soybean oil
0-Minimum
One or more of the following characteristics:
- Does not burn
- Does not reach flash point
- Does not burn when exposed to (815.5C(1500F) for 5 minutes.
Instability-Reactivity
4- Maximum
A substance that has one or more of the following characteristics:
- Can explode or decompose violently at ordinary temperatures and pressures.
- Can undergo a strong self-accelerating exothermic reaction with common materials or spontaneously.
- At ordinary temperatures and pressures, may be sensitive to mechanical or local thermal shocks.
Example: Nitroglycerin
3- Serious
Substances that have one or more of the following characteristics:
- Can explode or detonate. But requires a strong force to start or heat limited before the explosion begins.
- Easily accelerates oxidation with combustible materials and may cause a flame.
- Sensitive to thermal and mechanical shocks at high temperatures.
- May react explosively with water without the need for heat.
Example: Ammonium nitrate
2-Moderate
Substances that have one or more of the following characteristics:
- Normally unstable or readily undergoes violent changes but does not lead to an explosion.
- Undergoes chemical changes at ordinary temperatures and pressures that result in the release of energy.
- Reacts violently with water.
- A substance that, when reacted with water, forms a mixture that has the potential to explode.
Example: Phosphorus, Potassium, and Sodium
1-Mild
- A substance that is normally stable but can become unstable at high temperatures and pressures.
Example: Propane
0-Least
- A substance that is normally stable and does not react with water
Example: Helium
Note: This property is mostly concerned with the reaction with water during a fire.
Special Hazards
In the small white diamond, you may see one of the following symbols:
W A substance that reacts dangerously and unusually with water. (That is, if we pour water on this substance or pour it on water, we may cause an accident.)
OXY an oxidizing agent
ACID Indicates an acid
ALK Indicates a base
COR Indicates a corrosive substance
SA Indicates a simple asphyxiating gas. (Of course, this is not usually written.)
Uses of Hazard Symbols
One of the main tasks of occupational safety and health experts is to identify all materials entering their workplace (input materials), all intermediate materials, and all materials leaving the workplace, and to introduce their hazards to others by labeling them.
One of the most common ways to introduce hazards is to use appropriate safety signs and warnings (such as hazard symbols).
One of the parts of the Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) is the hazard symbol, which most reputable organizations in the world also include in their MSDS of chemical materials. You can use MSDS to identify the hazards of chemicals.
share :













Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.