Measuring Carbonate and Bicarbonate in Water: A Complete Guide to Alkalinity Control

Introduction: Why is water alkalinity important to industry?
Have you ever wondered why some industrial water heater systems or boilers lose their efficiency after a while? Or why pipes get clogged and maintenance costs suddenly increase? The answer to many of these questions lies in the alkalinity of water, especially in the concentration of carbonate (⁻CO²₃) and bicarbonate (⁻HCO₃) ions.
These ions not only affect the taste of water, but also play a key role in the formation of mineral deposits, corrosion of equipment and reduced efficiency of heating systems. In this article, you will learn about the basic concepts, measurement methods, industrial importance and alkalinity management solutions in a simple and practical way.
What are carbonates and bicarbonates?
Chemical definition
- Bicarbonate (⁻HCO₃): A polyatomic anion that is actually an intermediate form of carbonic acid (H₂CO₃). This ion is predominant at typical pHs of natural waters (between 6 and 8.5).
- Carbonate (⁻CO₃²): The fully deprotonated form of carbonic acid that is stable in more alkaline environments (pH above 10).
Both of these ions are formed from the decomposition of minerals (such as limestone) in soil or the absorption of carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere into water.
What is alkalinity and why is it important to measure it?
Definition of alkalinity
Alkalinity is the capacity of water to neutralize acids. In other words, the degree to which water resists a decrease in pH. This property is mainly determined by three ions:
1. Bicarbonate (⁻HCO₃)—the most common in natural waters
2. Carbonate (⁻CO₃²)
3. Hydroxide (⁻OH)
✍️ The general formula for alkalinity is as follows:
A = [HCO₃⁻] + 2 [CO⁻²₃] + [OH⁻] - [H⁺]
Note: Each carbonate ion has a double negative charge, so its effect on alkalinity is twice that of bicarbonate.
Why is alkalinity important?
- In industrial systems: High alkalinity leads to the formation of calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) scale, which reduces the efficiency of heat exchangers, boilers, and chillers.
- In water treatment: Alkalinity acts as a buffer and prevents sudden fluctuations in pH.
- In water supply networks: Deposits caused by high alkalinity cause clogging of pipes and increase maintenance costs.
Methods for measuring carbonate and bicarbonate
Acid-base titration: standard method
The common method for measuring alkalinity is titration with a standard acid (usually HCL or H₂SO₄). In this method, there are two important endpoints:
1. Phenolphthalein endpoint (pH ≈ 8.3)
- At this point, all the hydroxide and half of the carbonate are neutralized.
- The color of the solution changes from pink to colorless.
2. Methyl orange endpoint (pH ≈ 4.5)
- At this point, the bicarbonate and the other half of the carbonate are converted to carbonic acid.
- The color changes from yellow to orange.
Interpreting Titration Results
By comparing the volume of acid consumed in the two steps, the type of dominant ions can be identified:
Conditions | Type of alkalinity |
P = 0 | Only bicarbonate |
P < T/2 | Bicarbonate + Carbonate |
P = T/2 | Only carbonate |
P > T/2 | Carbonate + Hydroxide |
P = T | Hydroxide only |
Where:
P = Phenolphthalein alkalinity
T = Total alkalinity
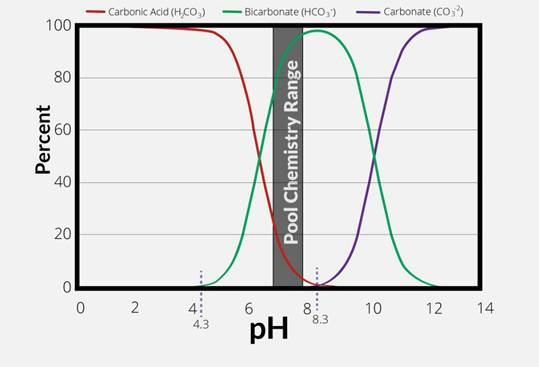
The effect of pH on carbonate balance
In water, the carbonic system
(H₂CO₃/ HCO₃⁻/ CO₃² ⁻)
is strongly dependent on pH:
- pH < 4.5: dominant= H₂CO₃ (carbonic acid)
- 4.5 < pH < 8.3: dominant=⁻HCO₃(bicarbonate)
- pH > 10.3: dominant= ⁻CO₃² (carbonate)
Therefore, in most natural waters (pH 6–8.5), bicarbonate constitutes more than 90% of the alkalinity.
⚡⚡⚡ Problems caused by high alkalinity in industry ⚡⚡⚡
1. Scaling
- ⁺Ca² and⁺Mg² ions react with⁻CO₃² to form calcium carbonate (CaCO₃).
- This hard, white scale forms an insulating layer on heating surfaces.
- Result: reduced heat transfer, increased fuel consumption, overheating and equipment failure
2. Reduced efficiency of heating systems
- In boilers, a 1 mm scale can reduce efficiency by up to 10%.
- In chillers and heat exchangers, water flow is restricted and pressure drops.
3. Increased maintenance costs
- Requirement for frequent chemical flushing
- Replacement of worn parts
- Stopping the production line for repairs
⭐⭐⭐ Solutions to manage alkalinity and scale prevention ⭐⭐⭐
1. Regular water analysis
Monthly or seasonal measurement of parameters:
- Total alkalinity
- Calcium and magnesium hardness
- pH
- Electrical conductivity (EC)
2. Use of water softeners
Replacing⁺Ca² and⁺Mg²ions with⁺Na through ion exchange resins.
3. Inject anti-scale chemicals
- Polyphosphates and polyacrylates prevent crystallization of CaCO₃.
- Mild acids (such as citric acid) to temporarily lower pH and dissolve existing scale.
4. Periodic chemical flushing
- Use acidic scale removers to clean circulating water systems.
- Perform compatibility tests before flushing to prevent corrosion.

Inside the heat exchanger before scaling

Inside the heat exchanger after chemical flushing
❓❓❓ Common User Questions ❓❓❓
❓ Does high alkalinity mean alkaline water?
No. Alkalinity ≠ pH .
- pH indicates the concentration of⁺H ions.
- Alkalinity indicates the capacity of water to resist pH changes.
❓ Can alkalinity be measured without a lab?
Yes, field titration kits (Field Test Kits) can give a rough estimate of total alkalinity, but lab equipment is needed to accurately detect carbonate and bicarbonate.
❓ When should the system be flushed?
- 10% reduction in thermal efficiency
- Increase in water outlet temperature
- Increase in pump pressure
- Water analysis reports show increased alkalinity and hardness
✅ Conclusion: The health of water systems starts with testing
Understanding and controlling water alkalinity — specifically the concentration of carbonate and bicarbonate ions — is not just a laboratory matter, but an economic strategy for industries. With a small investment in water analysis and smart planning for chemical washing, high repair costs, production downtime and energy consumption can be avoided.
If you are facing scaling, reduced efficiency or corrosion problems in your industry, expert advice and accurate water testing are the first step to a sustainable solution. Many industrial units, in collaboration with reputable laboratories, implement preventive maintenance programs that extend the life of equipment by several years.
⏳ What is your next step?
If you found this article useful, share it with your colleagues in the maintenance or operations department. You can also request a free guide to the "Water Circulation Systems Maintenance Checklist" via the contact form on our site.
☎️☎️☎️ Contacting drainage specialists ☎️☎️☎️
share :













Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.