MVC desalination plant (Mechanical vapor compression)

MVC is the smallest, most energy-efficient, and smartest desalination technology for small and medium-sized industries — but without proper chemical management, the smallest mistakes can cause the biggest losses.
In this expert guide, we’ll cover everything about MVC desalination — from how it works and benefits to chemical challenges and practical solutions — in simple, actionable language. And, finally, we’ll show you how to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and extend equipment life.
Why read this article?
✅ Gain a deep understanding of how MVC desalination works
✅ Identify its advantages and disadvantages in industrial applications
✅ Learn about the industries that use MVC the most and why
✅ Expert solutions for controlling scale, corrosion, and chemical washing of evaporators
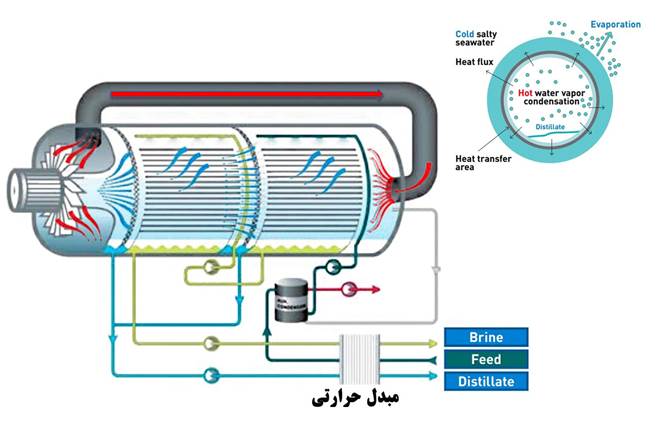
What is MVC desalination?
MVC stands for Mechanical Vapor Compression. A thermal technology that uses salt or brackish water to produce fresh water with very low energy consumption.
How MVC works:
- The salt water is heated and evaporated in the evaporator.
- The steam produced is compressed by a mechanical compressor and its temperature increases.
- The hot and compressed steam returns to the evaporator as a heat source and gives its heat to the incoming water.
- After condensation, the steam is collected as fresh water.
- The concentrated water (brine) is discharged from the system.
Key advantage: Closed system — no external heat source required — very low energy consumption.
Advantages of MVC desalination — why is it popular in small and medium industries?
1. Very low energy consumption (5 to 10 kWh per cubic meter of water)
- Only electricity required for the compressor — no steam or fuel required
2. Fully enclosed and compact system
- Suitable for confined spaces and mobile or remote projects
3. Automatic operation without the need for constant monitoring
- Advanced control systems — Ability to start up and maintain with minimal human effort
4. No need for external heat source
- Unlike MED or MSF, no need for steam or hot water — Suitable for industries without access to thermal energy
5. Very high outlet water quality (TDS < 10 ppm)
- Suitable for feeding boilers, laboratory uses and sensitive processes
Disadvantages and challenges of MVC desalination — What causes system failure?
1. Evaporator scale formation
- Formation of calcium carbonate, calcium sulfate and magnesium hydroxide on hot surfaces → Reduced heat transfer → Increased compressor load → Increased power consumption
2. Corrosion in compressor and pipes
- Presence of chlorides and dissolved oxygen → Corrosion of carbon steel and stainless steel — especially at high temperatures
3. Sensitivity to incoming water quality
- Highly hard or silica-containing water → Rapid scale formation — efficiency loss in less than 3 months
4. Relatively high initial cost (compared to RO in small capacities)
- Mechanical compressors and precise control equipment — increase investment cost
5. Need for periodic flushing with specialized chemicals
- Washing with strong acids → Damage to metals → Leakage and emergency shutdown
- Need for non-corrosive, temperature-compatible sedimentation vectors
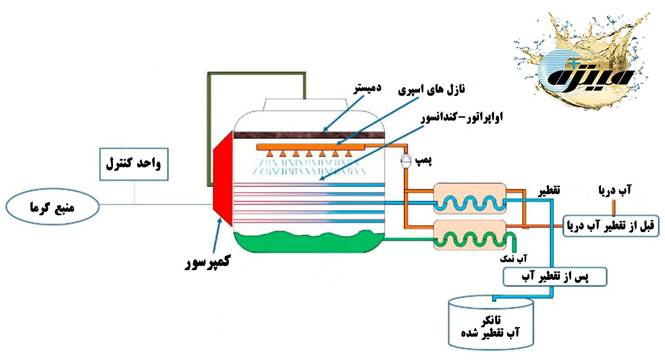
In which industries is MVC desalination used? And why?
1. Small and medium industries (capacity 100 to 5000 cubic meters per day)
- → Why?
- Need for high quality water without heavy investment
- Lack of access to steam or hot water
- Limited space for equipment installation
2. Remote and island projects
- → Why?
- Need for an independent and low-consumption system
- Possibility of power supply with generator or solar panel
- Easy transportation and installation
3. Food and pharmaceutical industries
- → Why?
- Production of high purity water for production and washing processes
- Continuous operation and no need for regeneration chemicals
4. Small power plants and steam generation units
- → Why?
- Production of high purity boiler feed water
- Cost reduction by using local salty or brackish water
When should the MVC system be flushed?
- 10-15% increase in compressor power consumption
- 10-20% decrease in fresh water production
- Increase in operating temperature in evaporator
- Increase in pressure in evaporation chamber
- Increase in vibration or noise in compressor or pipes
Golden tip:
Don’t wait for the system to experience a significant drop in efficiency! Periodic cleaning (every 6-12 months) can double the life of the equipment and reduce energy costs by up to 25%.
Final conclusion:
The MVC desalination plant is an energy-efficient, smart technology ideal for small and medium-sized industries — but without proper chemical management, it becomes a source of cost and reduced efficiency.
share :













Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.