Lithium Bromide Absorption Chillers: Application, Performance, and Maintenance Challenges

Introduction: Why are lithium bromide absorption chillers popular in industry?
In today’s world, energy efficiency and environmental sustainability are two key criteria when choosing industrial equipment. By using waste heat or steam instead of electricity, lithium bromide absorption chillers are an ideal choice for industries looking to reduce electrical energy consumption and increase thermal efficiency. But these systems are not without their challenges. From solution crystallization to metal corrosion, proper maintenance of these chillers requires technical knowledge and precise chemical solutions.
In this comprehensive and user-friendly article, we will examine how lithium bromide absorption chillers work, their unique features, advantages and limitations, and most importantly, chemical maintenance solutions to increase the life and efficiency of these systems.

What is an absorption chiller and how does it work?
Unlike compression chillers that use electricity to compress the refrigerant gas, absorption chillers use heat as the main energy source. This heat can be provided by steam, hot water, or even natural gas. Therefore, these systems are very cost-effective in industries that generate excess heat (Waste Heat).
Main components of lithium bromide absorption chiller
The absorption refrigeration cycle in these systems revolves around four main components:
1. Evaporator
2. Absorber
3. Generator
4. Condenser
There are also two vital pumps in the system:
- Refrigerant pump:to circulate water in the evaporator
- Absorber pump:to circulate the lithium bromide solution
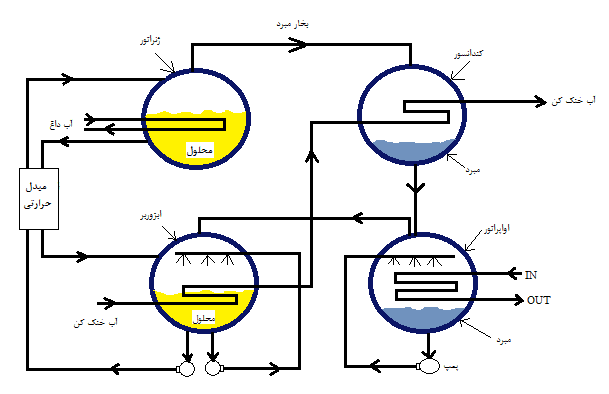
Lithium Bromide Chiller Absorption Refrigeration Cycle – Main System Components
Absorption Refrigeration Cycle: Step by Step
Step 1: Evaporation of Water in the Evaporator
In the evaporator, the pressure is artificially reduced to about 0.01 atmospheres. In this condition, the water begins to evaporate at a low temperature (about 4 to 7 degrees Celsius). This evaporation cools it by absorbing the latent heat of evaporation from the chilled water in the ventilation system.
Step 2: Absorption of Water Vapor by Lithium Bromide
The water vapor produced is quickly transferred to the absorber, where it is absorbed by a concentrated lithium bromide solution. This process is exothermic and requires cooling, usually with cooling tower water.
Step 3: Recovery of Water in the Generator
Over time, the lithium bromide solution becomes diluted and its absorption capacity decreases. For recovery, this dilute solution is pumped to the generator, where it is heated by external heat (steam or hot water). As a result, the water is separated as vapor and transferred to the condenser.
Step 4: Distillation and return of water to the evaporator
The water vapor in the condenser is re-liquefied using cooling water and returns to the evaporator to repeat the cycle. At the same time, the concentrated lithium bromide solution is returned to the absorber after passing through a heat exchanger.
This continuous cycle provides refrigeration without the need for a compressor.
Why lithium bromide and water? Ideal characteristics of an absorbent-refrigerant pair
The choice of absorbent and refrigerant pair is very critical in absorption chillers. The water-lithium bromide pair is a common choice for the following reasons:
- Large boiling point difference: water evaporates at a low temperature, while lithium bromide remains at a high temperature. This ensures that only water circulates in the cycle.
- High adsorption capacity: Lithium bromide has a strong tendency to adsorb water vapor, which reduces the need for large volumes of solution.
- Chemical stability: Within the operating temperature and pressure range, both materials are stable.
- Safety and environmental: Unlike ammonia systems, this couple is non-toxic and safe for urban and commercial environments.
Limitations of Lithium Bromide Absorption Chillers
Although these systems have many advantages, there are two main challenges that must be considered in the design and maintenance:
1. Crystallization of the lithium bromide solution
Lithium bromide tends to crystallize at low temperatures and high concentrations. These crystals can block pipes and pumps and cause the system to fail. To prevent this phenomenon:
- The temperature of the solution in the absorber must be carefully controlled.
- Intelligent control systems are used to regulate the temperature and concentration.
- Special care is required when starting and stopping the system.
2. Corrosion of metals in the system
Lithium bromide is corrosive, especially in the presence of oxygen and moisture. This corrosion can severely reduce the life of the equipment. Corrosion control strategies include:
- Maintaining a complete vacuum in the system to prevent oxygen from entering
- Use of corrosion inhibitors in the solution
- Continuous monitoring of pH and chemical concentrations

Corrosion in absorption chillers


Deposits in absorption chiller
Why is chemical maintenance of absorption chillers essential?
Many industries think that since absorption chillers operate without a compressor, they do not require complex maintenance. But the truth is that chemical maintenance of these systems is even more critical than compressor chillers.
Benefits of regular chemical maintenance:
- Increase thermal efficiency by up to 20%
- Reduce fuel or steam consumption
- Prevent unexpected shutdowns
- Increase equipment service life by up to 2 times
- Reduce maintenance costs
Chemical maintenance services to consider:
1. Regular analysis of solution samples (pH, concentration, presence of corrosive ions)
2. Periodic chemical flushing to remove deposits and corrosion layers
3. Anti-corrosion and anti-foam injection appropriate to the type of system
4. Check the vacuum of the system and eliminate possible leaks
5. Train operators to recognize early signs of crystallization or corrosion
When should an absorption chiller be flushed?
Chemical flushing should not be done only when a problem occurs. Rather, it should be planned proactively and based on operational conditions. Signs that indicate the need for flushing:
- Reduced cooling capacity without a clear technical reason
- Increased steam or hot water consumption
- Increased cold water outlet temperature
- Detection of solid particles or dark color in the solution
- Reduced system vacuum (air leakage)
In these cases, a comprehensive chemical analysis of the solution and internal surfaces is necessary to determine the type and severity of contamination.
Conclusion: Absorption chillers, a sustainable solution with smart maintenance
With their intelligent combination of heat and chemistry, lithium bromide absorption chillers are a sustainable solution for industrial-scale air conditioning. But their success is entirely dependent on careful chemical maintenance. Without proper corrosion and crystallization control, even a new system can fail within a few months.
If you use absorption chillers in your industry, investing in expert chemical advice and targeted flushing will not only reduce costs, but also optimize the efficiency of the entire system.
What’s your next step?
If you want to improve the performance of your absorption chillers, request a chemical analysis of your solution and system today. This simple task can add years of life to your equipment.
share :












Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.