Refrigeration cycles

Refrigeration Cycles
When a refrigerant circulates through a system, it goes through a number of changes of state or conditions, each of which is called a transformation. The refrigerant starts from an initial state and returns to its initial state after going through a series of transformations called cycles. Various refrigeration cycles are used to produce refrigeration, the most important of which are the compression refrigeration cycle, the absorption refrigeration cycle, and the thermoelectric refrigeration cycle.
Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle
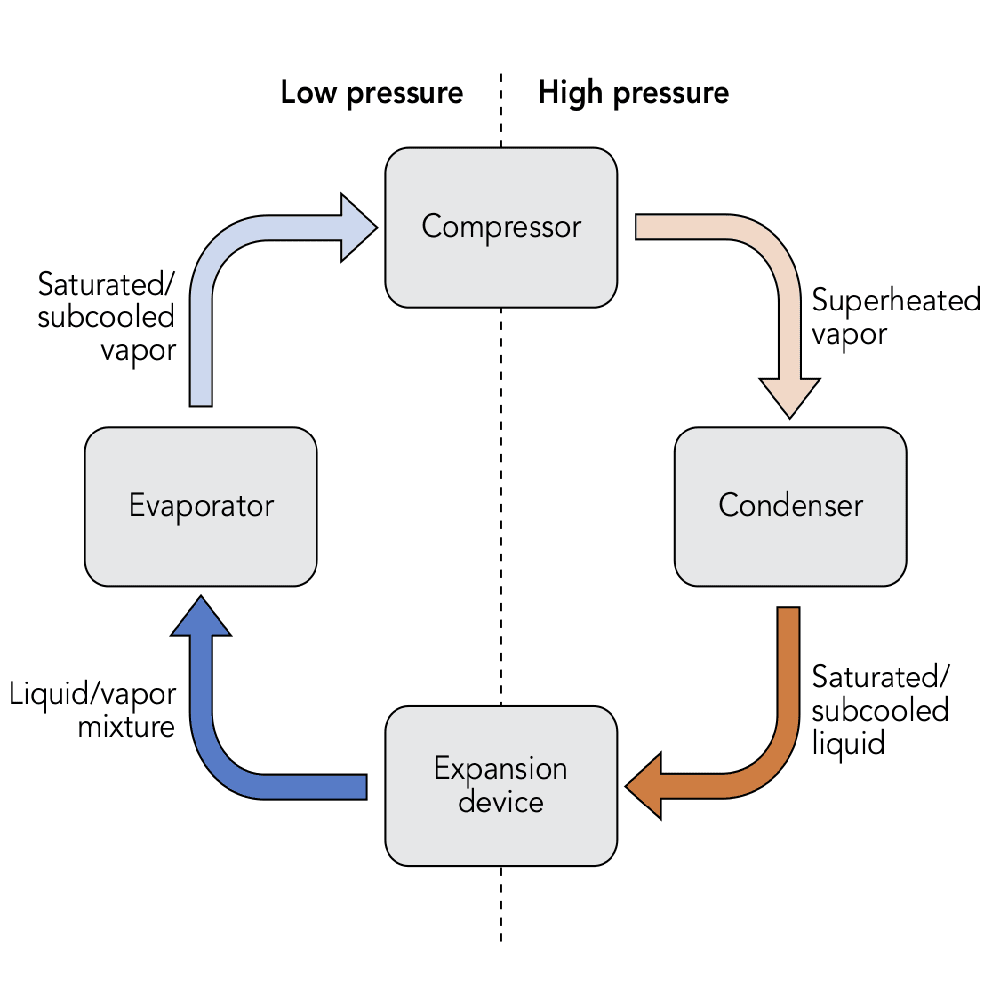
A schematic of an ideal vapor compression refrigeration cycle is shown in Figure (1-3). This cycle consists of the following four processes:
- Heat absorption at constant pressure in the evaporator
- Isentropic compression in the compressor
- Heat removal at constant pressure in the condenser
- Throttling in an expansion device
Absorption Refrigeration Cycle
An absorption refrigeration system is a system that works with the help of heat and heat. This system is very similar to a compression refrigeration system. (In a compression system, a centrifugal or reciprocating or rotary compressor is used). In both systems, we have an evaporator and a condenser. The process that occurs in the evaporator and condenser in both systems is at two different pressures so that refrigeration can be achieved in both cases. The difference between these two systems is in the way these two pressures are created for the evaporator and the distiller. These two systems also differ in the way the refrigerant circulates.
Absorption refrigeration system and its relationship to the compression refrigeration system
In a compression refrigeration system, the refrigerant evaporates at low pressure in the evaporator and takes the heat required for its evaporation from the surrounding environment. The compressor takes the vapor exiting the evaporator at the inlet and increases its pressure and directs it to the condenser. In the condenser, the vapor is distilled at high pressure and converted into a liquid. In an absorption system, the compressor function is replaced by a combination of an absorber unit or generator or steam generator.
The solution, which as an absorber has a high tendency to dissolve the refrigerant in it, moves between the steam generator and the absorber unit by a solution pump. In the absorber unit, the dilute solution dissolves the refrigerant vapor in itself, causing a low pressure to prevail in the evaporator so that the refrigerant can evaporate at a lower pressure. In the steam generator, the absorbent solution and the refrigerant are heated so that the refrigerant dissolved in the absorbent solution and the refrigerant separate from it and flow as high-pressure vapor to the condenser to be distilled there. Therefore, the suction operation in the compressor is replaced by the absorption operation in the absorber unit, and the pump has the task of raising the pressure of the refrigerant in the compressor and delivering the vapor to the condenser.
In a compression refrigeration system, the refrigerant vapor is directly transferred from the low pressure side (operator) to the high pressure side (condenser) by a compressor, while in an absorption system, the refrigerant vapor is absorbed in the absorber unit and the absorber and refrigerant solution are sent to the high pressure side (condenser-steam generator) by means of a pump. The refrigerant dissolved in the absorber is separated from the solution by the heat received in the steam generator. In fact, instead of increasing the gas pressure with a compressor, we dissolve it in an absorbent material and increase the pressure of the solution with a pump.
Therefore, the energy input for this system is the heat energy that is given to the solution in the steam generator. This energy can be in the form of hot water, steam or direct flame instead of using an electric motor or internal combustion engine in a compression refrigeration system. The figure below shows the alternative components of the compressor, and the working cycle.
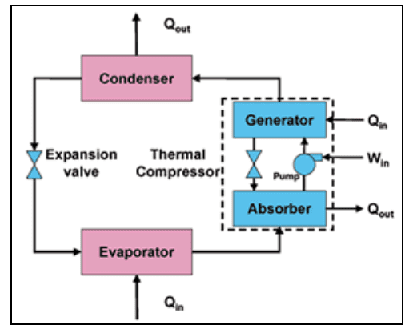
Absorption Refrigeration Cycle
share :









Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.