What is a chiller and what are its types? A comprehensive guide to choosing the best cooling system

Have you ever wondered how hospitals, large commercial complexes or petrochemical plants precisely control the temperature of their environment or industrial processes on the hottest days of the year? The answer to this question lies at the heart of an intelligent system called a chiller. Chillers are cooling machines that absorb the heat of the environment or industrial processes and transfer it to the outside by circulating cold water (or glycol solution). In this article, you will learn comprehensively about the types of chillers, how they work and their key applications in different industries.
How does a chiller work?
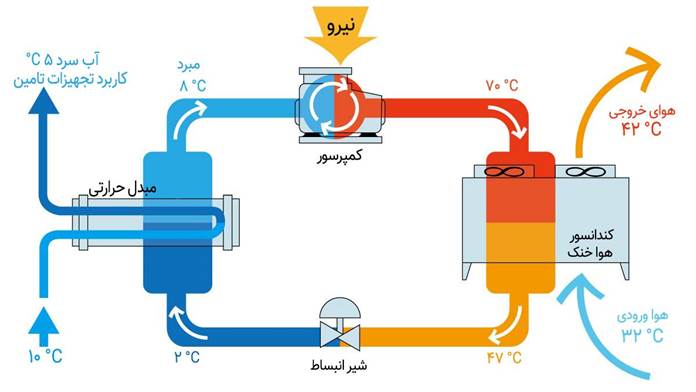
In the simplest case, chillers work based on two physical principles: vapor compression and heat absorption. In more common systems (vapor compression), a closed cycle consisting of four main stages is carried out:
1. Evaporation: The refrigerant in the evaporator absorbs the heat of the system water and evaporates.
2. Compression: The refrigerant vapor is compressed by the compressor and its temperature increases.
3. Condensation: The hot vapor in the condenser transfers its heat to the environment (water or air) and turns back into a liquid.
4. Expansion: The refrigerant liquid passes through an expansion valve, its pressure and temperature are reduced, and the cycle repeats itself.
Main types of chillers from the perspective of cooling method
The main difference between different chillers is the way in which the heat generated in the condenser is removed. This difference forms two main categories.
Water-Cooled Chillers
These types of chillers transfer the heat from the condenser to water. The heated water is then directed to a cooling tower, where it loses its heat to the air. Water chillers are ideal for large and industrial systems due to their higher efficiency and lower energy consumption compared to air-cooled chillers. Of course, the need for a water supply system and cooling tower increases their initial and maintenance costs.
✅ Advantages:
- Higher energy efficiency (especially in hot climates)
- Longer life
- Suitable for high capacities
❌ Disadvantages:
- Higher initial investment cost
- Requires more space for the cooling tower
- Requires a water supply and water management system (including anti-scale and anti-corrosion)
Air-Cooled Chillers
These chillers use air directly to cool the condenser. Powerful fans blow air over the tubes containing the hot refrigerant, transferring the heat to the environment. These systems are simpler, cheaper to install and maintain, and are a good option for locations where access to water is limited.
✅ Advantages:
- Easier installation and commissioning
- Lower initial cost
- No need for cooling tower and water supply system
❌ Disadvantages:
- Lower energy efficiency (especially in hot climates)
- More noise due to fans
- More sensitive to ambient temperature

Types of Chillers from the Perspective of Compressor Technology
In addition to the cooling method, the type of compressor also determines the performance, efficiency and application of the chiller.
Scroll Chillers
These chillers use a scroll compressor consisting of two fixed and moving scrolls. This design provides very quiet operation, high efficiency and low maintenance. Scroll chillers are usually used in small to medium capacities (up to about 200 tons of refrigeration) and are suitable for office buildings, small shopping malls and some industrial processes.
Screw Chillers
A screw compressor consists of two or more helical rotors that compress the gas towards the outlet. These types of chillers are ideal for medium to high capacities (between 100 and 1000+ tons of refrigeration). They have the ability to adjust the capacity and are widely used in large factories, hospitals and large residential complexes.
Absorption Chillers
Unlike other types, these chillers do not use a mechanical compressor. Instead, they use a heat source (such as steam, hot water, or natural gas) to separate the refrigerant from the absorber. Absorption chillers are economical when an inexpensive heat source or waste heat (such as exhaust heat from a gas turbine) is available. They are used in combined heat and power (CHP) systems and some heavy industries.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
Applications of different types of chillers in industries and buildings
The correct choice of chiller type depends on the specific needs of each project. Below, we will examine the common applications of each type.
Chillers in commercial and office buildings
- Screw or centrifugal water chillers:For large commercial complexes, hotels, and office buildings with high energy consumption, they are the first choice due to their excellent efficiency and low operating costs.
- Air-cooled chillers with scroll compressors:A good choice for smaller buildings or places where there is not enough space for a cooling tower.
Chillers in hospitals
Hospitals need very reliable and precise cooling systems. Water chillers with screw or centrifugal compressors are the most common choice due to their ability to provide continuous cooling and precise temperature control for operating rooms, laboratories and data centers.
Chillers in the food and beverage industry
In this industry, cooling is critical for processes such as pasteurization, fermentation, freezing and food storage.
- Scroll chillers:For smaller and medium-sized production lines such as dairies or juice factories.
- Screw chillers:For larger production lines and beverage factories that require high cooling capacity.
Chillers in the petrochemical and process industries
These industries need very powerful and durable cooling systems that can work in harsh conditions.
- Water chillers with screw or centrifugal compressors:To cool reactors, compressors and other process equipment.
- Absorption chillers:Where process waste heat is used as the energy source for the chiller.
❓❓❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) ❓❓❓
❓ What factors influence the selection of the type of chiller?
The three main factors are: 1) Initial budget and operating costs, 2) Availability of water and installation space, 3) Required cooling capacity and desired level of reliability.
❓ Why is water management critical in water chillers?
Circulating water in water chillers is prone to scale formation, corrosion and microbial growth (biofilm). These problems reduce efficiency, increase energy consumption and seriously damage the equipment. Therefore, the use of specialized chemical programs is essential to protect the system.
❓ What is the main difference between screw and scroll chillers?
Scroll chillers are designed for smaller capacities and lower noise, while screw chillers are more suitable for higher capacities and heavy industrial applications.
Conclusion: Smart cooling, the basis of sustainable performance ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐
The correct selection and maintenance of the chiller system not only ensures the comfort of residents or employees, but also leads to the efficiency of industrial processes and reduced energy costs. By understanding the different types of chillers and the applications of each, you can make an informed decision for your project.
If you need expert advice to identify the type of sediment or the optimal selection of chemicals, Abrizan Company specialists, with more than 20 years of experience in advanced laboratories, are ready to provide customized solutions to various industries.
share :













Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.