Water purification by electrodialysis method

Due to the shortage of water in the world, several methods have been proposed for separating dissolved salts from brackish water and seawater, including membrane methods including electrodialysis and reverse osmosis.
Electrodialysis device:
An electrodialysis (EDI) device consists of several main components, including: anionic and cationic membranes, electrodes, and polymer separators.

Membranes:
They are porous plates made of ion exchange resins and the type of ions passing through them can be selected.
Characteristics of membranes in an electrodialysis device:
- Impermeable to water under pressure
- Ability to selectively pass ions (positive or negative)
- Conduction of electric current
- Stability in aqueous solution
- Temperature stability above 45 degrees Celsius
- Stability against osmotic pressure
- Resistant to all types of sediments and sludge
Electrodes:
The type of electrodes used in an electrodialysis device is titanium or niobium with a platinum or palladium coating.
Polymer separators:
The membranes are separated from each other by polymer separators. Typically, the thickness of these meshes is half a millimeter in the space between the membranes and one millimeter next to the electrodes.
Electrodialysis method:
In the electrodialysis method, there are a series of water channels that are separated by anionic and cationic membranes. Since the basis of this method is the separation of charged particles, only charged particles are separated from water. In electrodialysis, cations and anions of salt water move towards the electrode with opposite charges. Therefore, when ions move towards the electrodes, cationic membranes prevent the movement of cations and anionic membranes prevent the movement of anions. Therefore, they are placed one between the anionic and cationic membranes and are formed one between fresh water and salt water drain between the membranes. The more salts the water contains, the more energy is required.
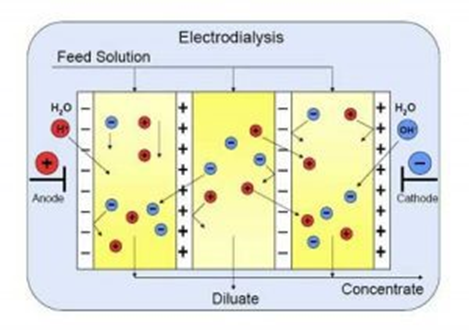
Schematic of water purification using electrodialysis
Advantages of the method:
If a membrane system is properly maintained, the membranes will be able to work for about 12 to 15 years. To eliminate membrane clogging, a new reverse electrodialysis system has been developed in which the positive and negative poles are alternately changed.
The most important advantages of this method are:
- Working with minimal membrane clogging
- Low pressure required
- Not affected by non-ionic compounds
- Less pre-treatment required than RO
The percentage of raw water conversion into purified water in electrodialysis is about 90%. That is, 90% of the incoming water is deionized and ions accumulate in the remaining 10%, which means that this wastewater must be disposed of properly. Because it may have adverse environmental effects.
Problems and disadvantages:
Since the membranes in the electrodialysis process are made of ion exchange resins, which are usually used in the form of one-meter-long plates (ion exchange resins are solid particles that can replace undesirable ions in the solution with the same amount of equivalent desired ions with the same charge), their properties change with the concentration of the environment and temperature, and even the type of ion, which causes a change in the efficiency of the membranes. Also, due to the creation of pinholes in the membrane, the selectivity of the membranes changes and, for example, a number of anions pass through the cationic membrane or vice versa.
This process is only able to remove dissolved minerals, and on the other hand, one of the problems of this method is the risk of sedimentation on the membranes. Therefore, the water must have passed the pre-treatment stages and be free of any suspended solids.
The electrodialysis process is a modern system and requires skillful maintenance and cleaning.
It is not suitable for treating water with a TDS higher than 500 ppm. And also in this method, it requires direct current with high voltage.
Water with high sulfate is difficult to purify in this method.
Important points in the design and operation of the system:
The temperature of the inlet water should not be less than 10 degrees Celsius and not more than 45 degrees Celsius.
The permissible limit of iron in the inlet water should be about 0.2 ppm. Because more than this amount increases the electrical resistance of the membranes and reduces the quality of the produced water and changes in the voltage and amperage used.
The presence of chlorine and hydrogen sulfide in the inlet water causes serious damage to the system and membranes.
In advanced systems, the cathode and anode poles should be moved every 15 minutes to automatically reduce deposits on the electrodes and clogging of the membranes.
The minimum system pressure is designed to be 15 atm and the maximum pressure is 1.5 atm.
To control the quality of the produced water, an electrical conductivity measuring device is installed at the outlet of the purified water.
If the system is stopped for more than thirty minutes, it is necessary to rinse the system every 4 to 8 minutes in order to drain the remaining salts and prevent deposits on the membranes.
Source:
Iranian Congress of Water and Wastewater Engineering Sciences
Comparison of Reverse Osmosis and Electrodialysis Methods in Water Treatment
share :













Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.