Water used in steel factories and its types

Water is used in most parts of a steel mill. A steel mill cannot operate without water. Hence, steel mills are typically built near abundant sources of fresh water to ensure the availability and quality of the water they require. However, today, special attention is paid to the management of water resources in the steel mill environment, especially in terms of its quality, quantity and how it is used.
A steel mill uses a large amount of water for steam generation, cooling, waste transport, dust control, etc. The processes of the mill cannot be carried out without water. A large amount of water is required for each stage of steel production. Less than 10% of this water is actually consumed and the rest of the water is usually returned to the system.
Several factors make water a very common material. It is easily transported, readily available, and inexpensive. Water can carry a large amount of heat per unit volume (high specific heat). Water neither expands nor contracts significantly over the ambient temperature range. Water does not decompose, which can cause dissolution, adsorption, suspension, and transport of other materials.
Despite the great importance of water in steel plants (Figure 1), the way water is used in steelmaking processes is not standardized, and there is no defined strategy or technique for measuring water in each process.
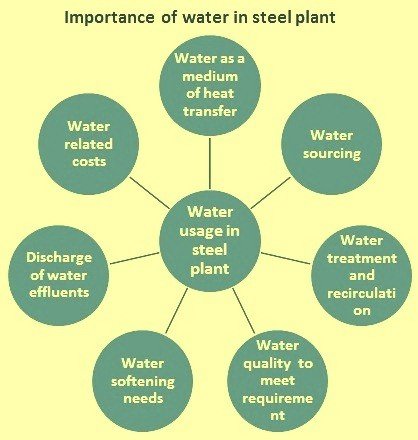
There are a number of aspects related to water and water-related technologies that are important for a steel plant:
Water is a medium for heat transfer and therefore is related to energy efficiency
The importance of providing water resources in terms of quality and quantity
Water monitoring, including re-treatment and recirculation systems
Water-related costs
Water quality depends on the process used
The effluent discharge process (chemical oxygen demand, suspended solids, biological oxygen demand, etc.) requires further standards
Water softening should be optimized based on step-by-step processes
The use of water can cause specific health and safety problems such as the spread of Legionella, as well as environmental problems.
Water is used directly for cooling and cleaning steel in the production process, for cooling exhaust gases, for washing the product, for forming solution in the process, etc. A large amount of water is used for indirect and non-contact cooling of process equipment. It is also used for steam and electricity generation, drinking water, and for dust and humidity control. In fact, in a steel plant, water performs a number of functions. The main functions of water in a steel plant are listed below:
A significant part of the water used in a steel plant is for cooling, including coke cooling, blast furnace shell cooling, cooling in casting and hot rolling machines. Almost every hot spot is cooled mainly using water.
Water is used for cleaning exhaust gases in coke ovens, blast furnaces, oxygen furnaces, etc.
Water is used in casting and in hot rolling operations. It is also used as a conveying medium to transport sediments to the sedimentation pit.
Water is used for heat treatment (thermal mechanical monitoring) in hot rolling mills.
Water acts as a source for steam generation.
Water is also used as an important part in chemical monitoring such as solvent in acid pickling, matrix for producing emulsions for rolling, cleaning, washing the surface of steel sheets, etc.
Water is used for electrochemical monitoring such as electro galvanizing or tinning, etc.
Water is used for dust suppression.
Depending on the use and quality of water, different terms are used in different locations of a steel plant: (i) raw water, (ii) potable water, (iii) rainwater, (iv) treated water, (v) (vi) direct cooling water, (viii) indirect cooling water, (ix) boiler feed water, (x) DM (demineralized) water, (xi) soft water, (xii) distilled water, (xiii) substitute water, (xiv) condensate water, (xv) drinking water, (xvi) fire water, (xvii) domestic water, (xviii) contaminated water, (xix) phenolic water, (xx) effluent and (xxi) sewage etc. Raw water is water that is available in natural sources such as (i) surface water sources (river, lake, reservoir and sea etc.) and (ii) groundwater sources. Sea water has high salinity and requires purification methods such as reverse osmosis etc. for its use in a steel plant. Groundwater is also analyzed because it may be saline. Raw water from sources other than the sea also requires treatment before it can be used in the steel mill. The degree of treatment required for the water depends on the characteristics and quality of the water available.
The intake water is the water that is pumped from the intake pump station located at the original raw water source. The factors determining the location of the intake pump are as follows:
As far as possible, this location should be close to the treatment facilities located at the steel mill to minimize the cost of transporting the water.
The intake should be located in the clean area of the source to produce the best quality water from the source, thereby reducing the load on the treatment section.
The intake should never be located downstream of or near the point of sewage disposal.
The site should allow for the discharge of more water if needed in the future.
The intake should be located in a location that can handle the water even during dry periods of the year.
The intake site should be easily accessible in the event of a flood and should not be subject to flooding. In addition, storm water should not be allowed to collect in the vicinity of the catchment.
Rainwater is diverted to the water treatment section in steel mills. This in turn helps to reduce water consumption and conserve natural resources.
Processed water is used for moisture control processes, temperature control processes, and for steel heat treatment. Processed water is also used for granulation of molten furnace slag. Another use of processed water is for cleaning and coating operations in cold rolling mills.
The major use of water in a steel mill is for cooling. Cooling water is generally classified as non-contact or indirect cooling water and contact or direct cooling water. Indirect use of water as a coolant is the use of water for general purposes where only the equipment is cooled and the water does not come into contact with the materials being processed, such as gases or liquids. Direct cooling water includes all applications where the water is in direct contact with the materials during the process, for cleaning process gases, process fluids (oil, cleaners, etc.) and for rinsing applications. Direct cooling water is treated for reuse in the system.
Boiler feed water is used to produce steam in the boiler. The raw water must be treated to the degree that it meets the quality required for steam production in the boiler. Such treatments typically include filtration, hardness removal (softening) and/or silica reduction, deaeration and pH/alkalinity adjustment. If treatment is not performed properly, water-related problems, including corrosion and mineral deposits, can cause permanent damage to the steam generation unit as well as inefficient energy transfer operations.
DM water is water from which the minerals in the water have been removed. DM water is also used as a boiler feed water. The demineralization process is usually performed when water is used for chemical processes and the minerals present may come into contact with other chemicals. Using the demineralization process, water is softened by removing unwanted minerals. DM water has a higher conductivity than deionized water.
share :







Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.