
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) test
Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Method
Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) can be used to investigate mechanisms, investigate coating uniformity, study inhibitor performance, and the continuity and durability of the inhibitor layer. In this method, a sinusoidal alternating current (AC) signal is usually applied to the system and then the current response is measured. This method is a non-destructive method due to the very low voltage amplitude.
Application of impedance testing
In general, impedance testing is used to investigate the value of charge transfer resistance on the metal surface in the presence and absence of an inhibitor. This test is especially suitable for obtaining rapid and accurate corrosion rates. The simplest electrical equivalent circuit to explain the electrochemical behavior of a metal in an inhibitor solution is the Randle 1 circuit according to Figure (1), which consists of the solution resistance (RS), charge transfer resistance (Rct), and double layer capacitance (Cdl). The output of the analysis is shown as a Nyquist plot, where the real part of the impedance is plotted along the x-axis and the imaginary part is plotted along the y-axis. The measured efficiency from the impedance test can be calculated according to the following equation:
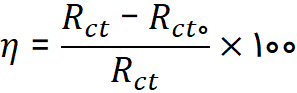
In this relation, Rct is the charge transfer resistance in the presence of the inhibitor, Rct0 is the charge transfer resistance in the absence of the inhibitor, and η is the inhibitor efficiency.
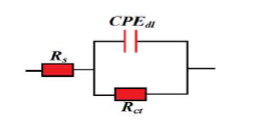
Figure (1) Equivalent circuit for analyzing electrochemical impedance spectroscopy test data
Equivalent circuit for analyzing impedance test data
Some inhibitors reduce the corrosion rate by forming a coating layer on the metal surface, in which case the equivalent circuit corresponding to this behavior will be as shown in Figure (2). In this circuit, RS is the solution resistance, Rf is the coating layer resistance, Rct is the charge transfer resistance, CPEf is the coating layer capacitance, and CPEdl is the double layer capacitance. Also, Rct obtained from this equivalent circuit is used to calculate the inhibition efficiency.
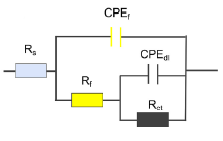
Figure (2) Equivalent circuit for analyzing electrochemical impedance spectroscopy test data
Performing impedance testing in Abrizan Laboratory
The laboratory of Abrizan Industrial Research Company is equipped with a potentiostat/galvanostat model Autolab PGSTAT302N to perform all electrochemical impedance spectroscopy tests. The professional experts of this company, with scientific support and experience gained from years of industrial activity, are able to simulate various process environments and evaluate the corrosion behavior of widely used industrial alloys under various conditions, such as the presence of corrosion inhibitors and coatings, with very high accuracy.

