
Polarization test with Autolab PGSTAT302N potentiostat/galvanostat device
Definition of Polarization Test
Polarization tests are among the electrochemical methods in the study of the kinetics of corrosion reactions. In fact, the deviation of the electrode from the equilibrium potential is called polarization, which can occur due to the application of external current or due to events on the electrode surface or in the electrolyte environment. (Activation polarization, concentration polarization, resistance polarization)
Polarization methods and their diagrams
In these tests, the working electrode in the desired environment is polarized using a potentiostat-galvanostat device relative to the reference electrode and the open circuit potential of the electrode, and the results are plotted on E-I or E-logi diagrams. These types of diagrams are called polarization diagrams. Polarization tests include three methods, the difference between which is in the polarization potential range.
- Linear polarization
- Potentiodynamic polarization
- Cyclic polarization
Measuring corrosion rate
Two methods can be used to measure corrosion rate: weight loss and polarization. The weight loss method is performed by immersion tests. To calculate corrosion rate by polarization method, first the polarization curve (E-Log i or E-i) consisting of two anodic and cathodic branches must be drawn using potentiostatic or potentiodynamic methods. For this purpose, it is first necessary to determine the electrode open circuit potential (OCP) in the electrolyte medium, then by applying a potential at a certain rate to the reference electrode, the electrode potential is changed from anodic potentials (lower than OCP) to cathodic potentials (higher than OCP), and then by drawing polarization diagrams, the electrode corrosion current density (icorr) is determined by linear polarization or Tafel extrapolation. After that, the corrosion rate can be determined using Faraday's equation.
Corrosion rate = Micorr/ρnF
Atomic weight of metal = M
Corrosion current density = icorr
Number of electrons lost = n
Faraday's constant = F
Electrode density = ρ
The corrosion rate measured by this method is more accurate than the weight loss method, but it is not as simple. Because polarization tests are among the electrochemical methods in the study of corrosion, their implementation requires taking into account several considerations.
As mentioned, the corrosion current density can be obtained directly from the Tofel diagrams. For this purpose, initially, about ± 50 millivolts should be moved from both sides relative to the open circuit potential and after passing through these two ranges, by selecting appropriate points to draw the anodic and cathodic slopes, the current obtained from the intersection of these two slopes should be obtained as the corrosion current density.
Calculation of the inhibitory efficiency
It should be said that using the corrosion current density and the following formula, the inhibitory efficiency can be calculated:
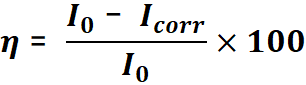
In this relation, I0 is the corrosion current density in the absence of the inhibitor, Icorr is the corrosion current density in the presence of the inhibitor, and the 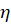 inhibitory efficiency.
inhibitory efficiency.
Conducting Polarization Tests in Abrizan Laboratory
The laboratory of Abrizan Industrial Research Company is equipped with a potentiostat/galvanostat model Autolab PGSTAT302N to perform all polarization tests. The company's professional experts, with scientific support and experiences gained from years of industrial activity, are able to simulate various process environments and evaluate the corrosion behavior of widely used industrial alloys under various conditions, such as the presence of corrosion inhibitors and coatings, with very high accuracy.

