Types of boilers and their applications in industry

Introduction: What is a boiler and why is it important to choose the right type?
A boiler is a device that converts water into steam using fuel (such as gas, oil or biomass). This steam is used in various industrial processes, including electricity generation, heating, drying, sterilization and distillation.
But not all boilers are the same. The type of boiler should be selected according to the required capacity, working pressure, available space, fuel type and operating conditions. The wrong choice can lead to reduced efficiency, increased fuel consumption, production stoppages and safety hazards.
In this article, we will get acquainted with the main types of boilers in a general and overview and review the applications of each. For more specialized information about each type, you can refer to our detailed articles.
General classification of boiler types
Boilers are classified according to various criteria, but the most important division is based on the internal structure and the way hot water and gas flow. Below, we will introduce the main types of boilers:
Fire Tube Boilers
In this type, the flame and hot gases pass through the tubes and the water is around the tubes. These boilers are very common in small and medium industries due to their simple design, low cost and quick installation.
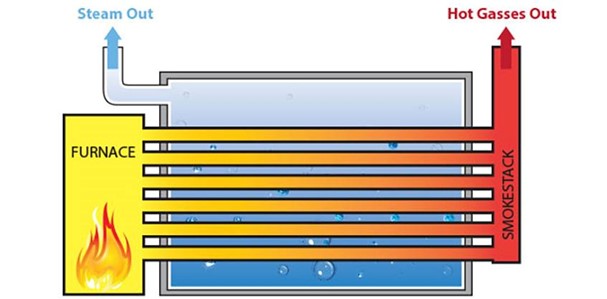
Fire tube boiler applications:
- Food and textile industries
- Hospitals and hotels
- Heating systems
Advantages of fire tube boilers:
- Low initial cost
- Less manpower requirement
- High safety
Disadvantages of fire tube boilers:
- Limited capacity and pressure
- Sensitivity to water quality
Water Tube Boilers
In this type, water flows inside the tubes and the flame passes outside the tubes. These boilers are capable of producing steam at very high pressure and capacity and are used in large industries.

Applications of water tube boilers
- Thermal power plants
- Large refineries
- Petrochemicals
Advantages of water tube boilers:
- High efficiency
- Possibility of producing superheated steam
- Better safety than Fire Tube
Disadvantages of water tube boilers:
- High initial and maintenance cost
- Requires specialized personnel
HRSG (Heat Recovery Steam Generator) boilers
These boilers do not have a burner and use the heat of the hot gases exiting the gas turbine to produce steam. They are used in a combined cycle.
HRSG Boiler Applications:
- Gas-fired power plants
- CHP (combined heat and power) units
Advantages of HRSG Boilers:
- Heat recovery and increased overall system efficiency
- Reduced fuel consumption
- Less pollution
Disadvantages of HRSG Boilers:
- Dependent on gas turbine
- Complex design
Package Boilers
These boilers are delivered completely and pre-assembled. They are usually of the Fire Tube type and are suitable for small industries.

Package Boiler Applications:
- Small Manufacturing Units
- Commercial Buildings
- Semi-fluid Industries
Advantages of Package Boilers:
- Quick and Easy Installation
- Small Space Occupancy
- Automatic Control
Disadvantages of Package Boilers:
- Low Flexibility
- Limited Capacity
Vertical Boilers
Have a vertical structure and occupy little space. They are usually used in small applications and limited spaces.
Vertical boiler applications:
- Ships and vessels
- Laboratories
- Industrial steamers
Advantages of vertical boilers:
- Small space
- Light weight
- Easy installation
Disadvantages of vertical boilers:
- Very low capacity
- Average efficiency
Once-Through boilers
These types of boilers are drumless and water passes through the pipes once and turns into steam. They are designed for supercritical pressures and advanced power plants.
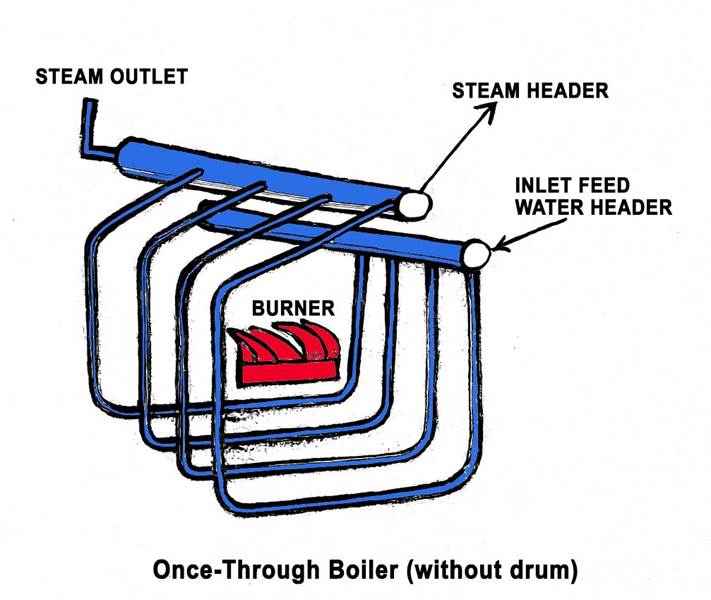
Applications of Once-Through Boilers:
- New Generation Power Plants
- Very High Pressure Units
Advantages of Once-Through Boilers:
- Very High Efficiency
- No Risk of Drum Explosion
Disadvantages of Once-Through Boilers:
- Very High Cost
- Requirement of Ultra-Purified Feedwater
How to Choose the Right Type of Boiler?
For optimal selection, consider the following:
- Required Steam Capacity (tons per hour)
- Steam Pressure and Temperature
- Available Space for Installation
- Type of Fuel Available (Gas, Oil, Biomass)
- Initial Cost and Maintenance
- Requirement of Expert Personnel
In large industries, Water Tube and HRSG are the main options, while in small industries, Fire Tube and Package are more popular.
Importance of Maintenance and Feedwater Quality
Every type of boiler, regardless of its type, requires feedwater quality and periodic maintenance. Scale and corrosion can:
- Reduce efficiency
- Increase fuel consumption
- Shorten equipment life
The use of water pretreatment, specialized chemicals, and periodic chemical flushing (with products such as Mitreh) is key to optimizing performance.
Summary
- Fire Tube: Suitable for small and medium-sized industries
- Water Tube: The main choice in large power plants and refineries
- HRSG: For heat recovery in a combined cycle
- Package: For fast installation and limited space
- Steam generator: For very high pressures
The correct choice of boiler type has a direct impact not only on efficiency, but also on safety, operating costs, and equipment life.
share :













Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.