Water chloride measurement
The chloride ion is a chlorine anion that forms the negatively charged part of some salts, including sodium and hydrogen chloride salts. Chloride, also known as the chloride ion or –¬Cl, is in the group of inorganic compounds known as the homogeneous halogens. In fact, nonmetallic compounds are inorganic
What is chloride ( - Cl )?
Chloride ion is a chlorine anion that forms the negatively charged part of some salts, including sodium salts and hydrogen chloride. Chloride, also known as the chloride ion or –Cl, is in the group of inorganic compounds known as the homogeneous halogens. In fact, non-metallic compounds are inorganic.
Difference between chlorine and chloride
Chlorine is produced commercially and is best known for its use in compounds for water purification and the creation of cleaning products. Chloride is actually formed when chlorine gains electrons and combines with other elements. Chloride is the negatively charged chlorine ion with the molecular formula Cl–, and chlorine is known as Cl2.

Uses of Chloride
Sodium chloride is widely used in the production of industrial chemicals such as caustic soda, chlorine, sodium chloride and sodium hypochlorite. Sodium chloride, calcium chloride and magnesium chloride are widely used in snow and ice control. Potassium chloride is used in the production of fertilizers.
Does chloride cause corrosion of metals?
Chloride ions in water cause localized corrosion such as crevice and pitting corrosion, and the higher the chloride content, the more corrosive the water is. The chloride concentration in water passing through wastewater treatment plants is usually lower than the chloride concentration in seawater.
Chlorides are particularly corrosive compounds for many metals. The solubility of metal chlorides in water is relatively high, and since chloride is monovalent, it tends to stabilize suspended solutions, thereby preventing the formation of a protective layer of corrosion product. Chlorides are present in high concentrations in seawater and are dispersed into the air by wind blowing over the water. However, over time, they dry out and become fine solid particles. As a result, areas near the ocean are highly corrosive to most metals. Steels and, to a lesser extent, copper alloys are more affected by chlorides, while zinc and nickel are less affected.
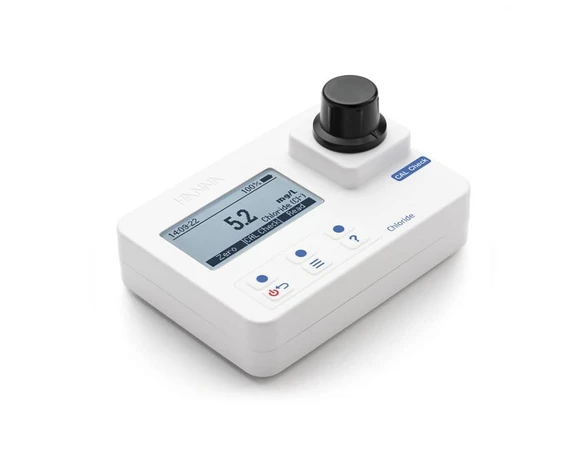
The laboratories of Abrizan Industrial Research Company, located in Fars Science and Technology Park, are capable of measuring various water parameters, including chloride, using advanced devices and equipment.