Caustic corrosion

Caustic (caustic salt)
Caustic soda is one of the most widely used ionic compounds and is used in various industries including water treatment, cardboard and paper production, oil and refinery industries, aluminum production, food, alcohol and glass industries. These compounds are available in liquid and solid form and in white flakes. This compound has a very high alkalinity and also has a very high dissolving power and leads to chemical burns on the skin and its excessive use in equipment causes corrosion in facilities.
Caustic corrosion
Localized corrosion caused by concentrations of caustic salts (caustic soda) or alkalis, usually occurring under conditions of high evaporation or heat transfer. However, general corrosion can also occur depending on the strength of the alkaline or caustic solution.
Materials affected by caustic corrosion
Primarily carbon steel, low alloy steels and 300 series SS
Vital factors
The main contributing factors are the presence of caustic materials (NaOH or KOH). The following are sources of caustic:
- Caustic is sometimes added to process streams for neutralization or as a reactant.
- Sometimes intentionally added to boiler feed water in low concentrations or may be introduced unintentionally during mineral regeneration.
- Alkaline salts may also enter the process stream through leaks in condensers or process equipment.
- Some process units use caustic solutions for neutralization, removal of sulfur compounds, or removal of chloride compounds.
- A centralized mechanism must exist to generate caustic power.
- Caustic may concentrate as it exits the DNB, evaporate, and precipitate.
Damaged units or equipment
- Caustic corrosion is often associated with boilers and steam generating equipment, including heat exchangers.
- Accelerated localized corrosion can occur in preheat exchangers, furnace tubes, and transfer lines unless the caustic is effectively mixed into the oil stream.
- Units that use caustic materials to remove sulfur compounds from the product stream.
Appearance and morphology of the injury
It is usually characterized by localized metal loss, which may appear as grooves in the boiler tube or localized thinned areas under insulation deposits.
Deposits may fill in corroded depressions and cover up underlying damage. Probing suspicious areas with a sharp instrument may be necessary.
Localized pitting may occur along water lines where corrosive materials concentrate. In vertical pipes, this may appear as a circumferential groove.
In horizontal or inclined pipes, corrosion grooves may appear at the top of the pipe or as longitudinal grooves on opposite sides of the pipe.
Exposure to highly caustic solutions can result in general corrosion of carbon steel above 79°C and very high corrosion rates above 93°C.
Preventing / reducing caustic corrosion
In steam generating equipment, caustic corrosion is best prevented by proper design. Damage can be minimized by reducing the amount of free caustic, by ensuring adequate flooding and water flow, by ensuring proper burner management to minimize hot spots on the heater tubes, and by minimizing the ingress of alkaline salts from the producer into the condenser.
In process equipment, caustic injection facilities must be designed to allow for proper mixing and dilution of caustic materials to prevent caustic material from concentrating on hot metal surfaces.
Carbon steel and 300 series SS have serious corrosion problems in high-strength caustic solutions at 150°F (66°C). Alloy 400 and some other nickel-base alloys exhibit much lower corrosion rates.
Inspection and monitoring
For process equipment, UT thickness gauges are useful for detecting and monitoring general corrosion caused by caustic materials. However, locating localized damage caused by caustic corrosion can be difficult.
Injection points must be inspected in accordance with API 570.
UT scans and radiographs can be used.
Steam generating equipment may require visual inspection using a borescope.
Related mechanisms
Caustic corrosion is also called caustic pitting or brittle pitting. A related mechanism is known as denucleation from weld (DNB), as discussed in Vapor Coating.
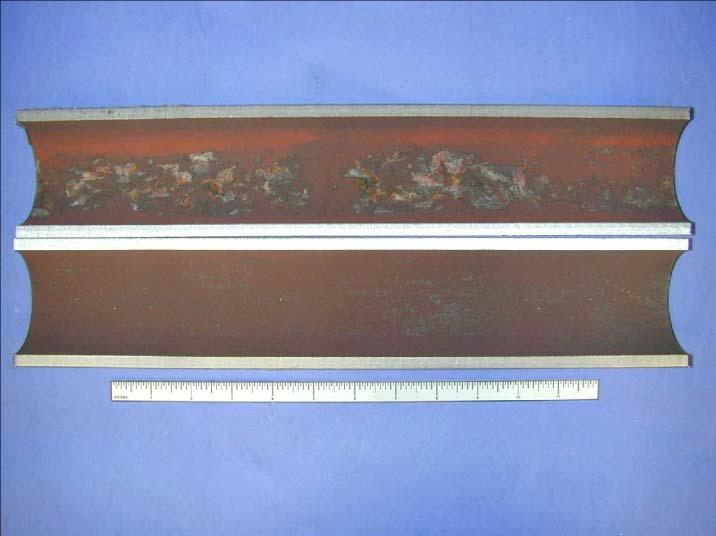

Internal diameter of scale on CS boiler tube with caustic corrosion damage
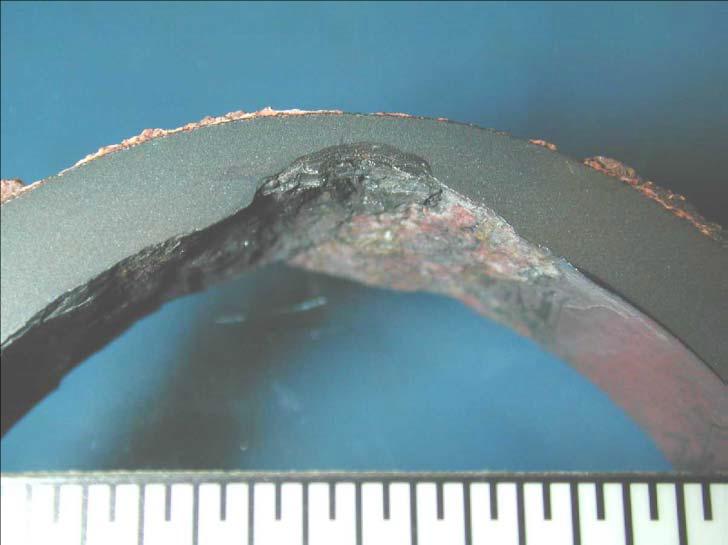
The cross-section of the pipe in the figure shows localized attack caused by caustic corrosion.
share :















Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.