Corrosion control

The effect of lithium bromide on corrosion of metals
The concentration of LiBr in solution can significantly affect the rate and severity of corrosion in metals. The concentration of lithium bromide can increase the corrosion rate, affect the pH of the solution, the formation of corrosion products, the solubility of oxygen, the effects of temperature, and also cause specific metal reactions.

Caustic corrosion
Localized corrosion caused by the concentration of caustic or alkaline salts, which usually occurs under conditions of high evaporation or heat transfer. Caustic salt or caustic soda is one of the most widely used ionic compounds and is used in various industries including water treatment, cardboard and paper production, oil and refinery industries, aluminum production industries, food industries, alcohol production and glass.

Corrosion and deposition of cooling water based on API 571
It refers to general or localized corrosion of carbon steels and other metals caused by dissolved salts, gases, organic compounds, or microbiological activity.
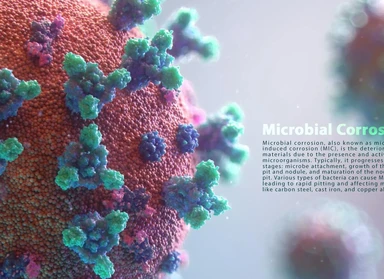
Microbial corrosion based on API 571
Microbial corrosion is a type of corrosion caused by living organisms such as bacteria, algae, or fungi. This type of corrosion is often associated with tubercles or slimy organic materials.

Dealing with corrosion in the well with corrosion inhibitors
Downhole corrosion is one of the most important problems facing the oil and gas industry. By using various methods such as selecting appropriate materials, surface coating, use of corrosion inhibitors and cathodic protection, the corrosion rate can be significantly reduced. A better understanding of corrosion mechanisms and the development of new technologies can help improve efficiency and reduce costs in this industry.

Industrial Mitreh (sediment remover and anti-corrosion)
Any system where temperature and water are the main elements for its operation inevitably requires the invention of Abrizan Company, called Industrial Mitreh, because wherever there is temperature and water, the formation of sediment is inevitable, unless a substance is used that suspends these sediments. This is the main function of an excellent anti-sediment solution.

The effect of various factors on metal corrosion
The set of factors affecting metal corrosion can be divided into two main categories: environmental factors and intrinsic factors of the metal.

Proper corrosion management
In general, it can be said that the corrosion process will never stop, but it can be controlled to a large extent by implementing a corrosion management program. In fact, by implementing corrosion management, organizations can proactively plan to improve the way they design, operate, and maintain their critical assets, thereby reducing the cost of controlling damage and unexpected failures caused by corrosion.

History of corrosion and scientific approach to corrosion
Is corrosion taking your industrial equipment out of service? Discover scientific and practical solutions for controlling and preventing corrosion in boilers, chillers, exchangers and water circulation systems.

Corrosion measurement units
In general, to facilitate the study of corrosion problems and to compare different metals with each other, the best method is to express the speed or rate of the corrosion reaction. Corrosion measurement units are used to express corrosion rates.

Cold Mitreh
Cold Mitreh, a water-soluble solution with a high dissolution rate, is introduced as a powerful scale remover and an innovative product of Abrizan Company. Cold Mitreh was developed in response to the industry's need for an alternative solution to descalers. Descalers are scale removers based on hydrochloric acid and are highly dangerous, toxic, and corrosive.

Corrosion costs and corrosion economics
Failure to pay attention to corrosion problems in any industrial and manufacturing unit results in hidden costs that are impossible to avoid. Economic considerations are essential in each of the corrosion control methods. Of course, there is no need to choose the most expensive corrosion control methods, because the costs incurred may not be economically justified and waste capital.

Causes of tube corrosion in the economizer of the steam generation system
Corrosion in steam generation systems causes many problems in refineries, gas plants and petrochemical plants. Corrosion in boilers is a function of the concentration of oxygen, carbon dioxide and ammonia and the way these species are controlled, and in some cases is caused by the presence of hydroxide and chloride anions or high concentrations of chelating chemicals in the boiler water.

Investigating the phenomenon of corrosion in the cooling tower and its control
Corrosion is one of the most important problems in the cooling tower and causes cost loss and reduced efficiency of the tower. The presence of various factors in the tower makes it easy for corrosion to occur in the cooling tower. The presence of water as an electrolyte and also the presence of metals of different types in the tower as cathode and anode provides the basis for creating a chemical cell on a large scale.

Corrosion in boilers
Corrosion in steam boilers is caused by chemical and electrochemical reactions of metal with its surrounding environment. The most important corrosion factors in steam boilers are oxygen corrosion, carbon dioxide corrosion, corrosion due to pH drop, alkalinity corrosion, corrosion of hydrolyzable salts and corrosion of organic materials.

Corrosion mechanisms of hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is an almost stable gas in the range of temperatures and pressures used in oil and gas exploitation systems, although in the presence of strong oxidants such as O2 and + Fe3, it can turn into elemental sulfur, which usually occurs in gas pipelines. It happens with high pressure or storage facilities. Hydrogen sulfide in concentrations higher than 80% is also found in some oil and gas reservoirs.
