Complete guide to chemical washing of industrial equipment Methods, detergents and safety tips

Introduction: The Importance of Chemical Cleaning in Industries
In today's industrial world, efficiency, safety, and equipment longevity are key factors in reducing operating costs and increasing competitiveness. One of the most important challenges faced by almost all industrial units is the formation of deposits within heat transfer systems, cooling systems, piping, and process equipment.
Deposits—the accumulation of mineral, organic, or biological materials on internal surfaces—not only reduce heat transfer efficiency, but also increase pressure drop, subsoil corrosion, increase energy consumption, and even complete equipment failure. According to global statistics, about $45 billion is spent annually due to energy loss caused by deposits in various industries.
In these circumstances, chemical cleaning and descaling are known as one of the most effective preventive maintenance solutions. This process allows for deep and safe cleaning of equipment without the need for physical disassembly or long system downtime.
In this article, we will review the types of chemical cleaning methods, commonly used detergents, safety precautions, reference standards, and industrial applications. We will also introduce one of the new and safe methods — cold Mitreh solution chemical cleaning (MDA0102) — as a sustainable and effective alternative to traditional methods.
What is scale and why is it dangerous?
Scale is a material that forms over time in water, heating, and refrigeration systems. It is mainly composed of water-soluble salts such as calcium carbonate (CaCO₃), calcium sulfate (CaSO₄), silicates, iron oxides, and corrosion products.
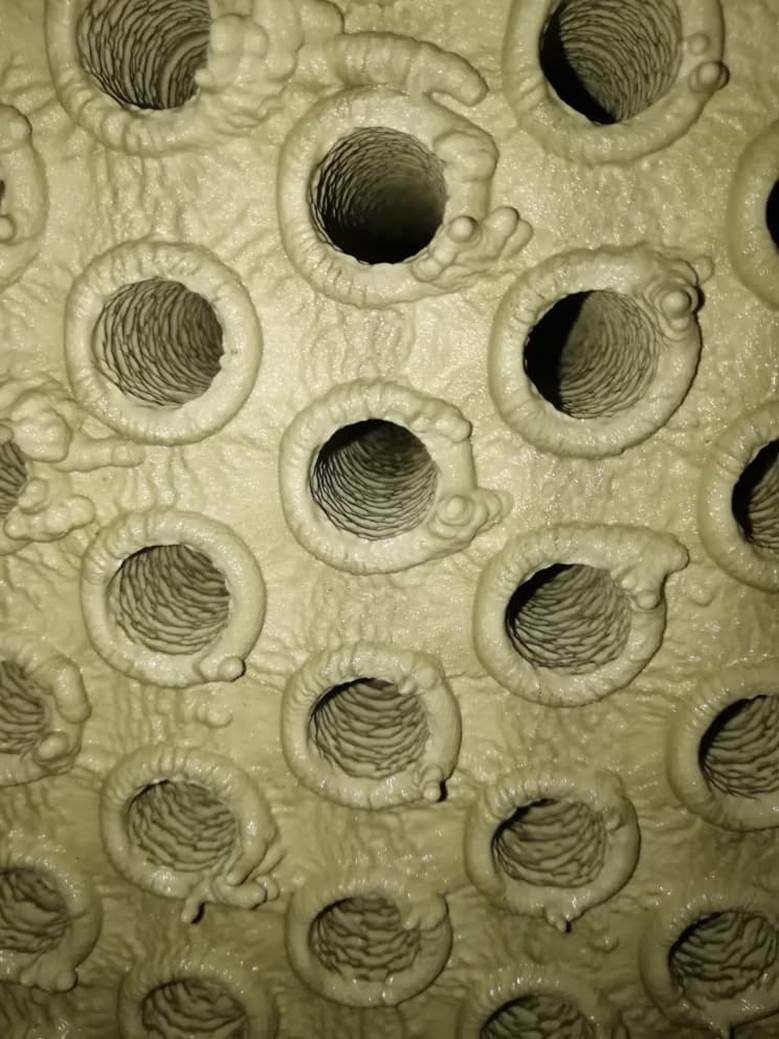
Main types of sediments:
- Crystalline sediment (such as calcium carbonate):The most common type in aquatic systems
- Particulate sediment:The accumulation of suspended particles in water (mud, sand, dust)
- Corrosive sediment:The formation of iron and copper oxides due to metal contact with water and oxygen
- Biological sediment:The growth of bacteria, fungi, and algae (biofilm)
- Chemical sediment:The formation of new compounds due to changes in temperature or pH
Consequences of scale formation:
- 20 to 70% reduction in heat transfer coefficient in exchangers
- 20 to 60% increase in system pressure drop
- Increased energy and fuel consumption
- Reduced flow rate and need for more pump power
- Under-deposit corrosion
- Clogging of pipes, nozzles and packings
- Reduced useful life of equipment
What is chemical washing?
Chemical washing is a process in which a chemical solution (usually acidic or alkaline) is circulated through or applied to industrial equipment to dissolve and remove deposits and contaminants adhering to internal surfaces.
This method has the following advantages:
- Access to inaccessible areas for mechanical methods
- Reduced production downtime
- Possibility of cleaning in place (CIP) without the need for complete disassembly of the equipment
- Removal of deposits without serious damage to the main structure of the equipment (if the chemical is selected correctly)
Main applications include:
- Heat Exchangers
- Boilers and Steam Boilers
- Cooling Towers
- Piping and Fluid Transfer Lines
- Chemical Process Systems
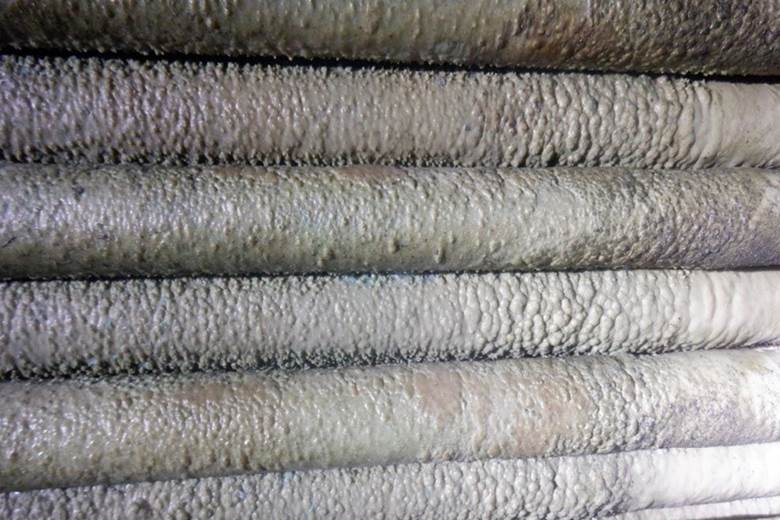

Before chemical washing of the thermal desalination plant of the third South Pars refinery
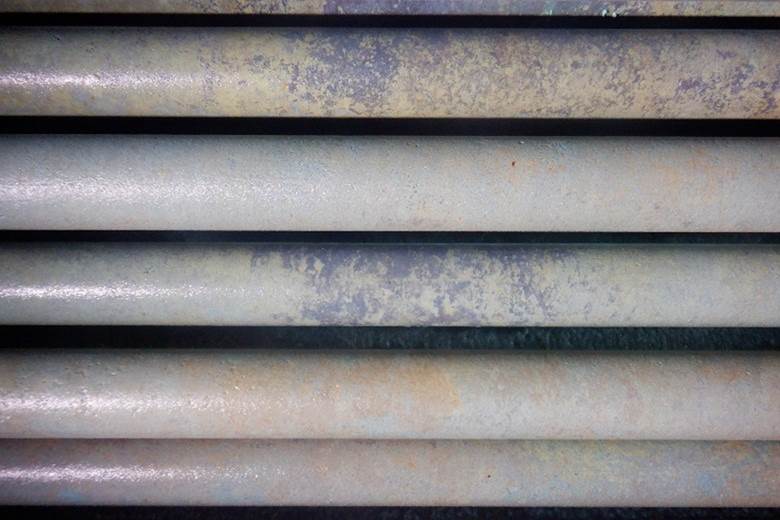

After chemical washing of the thermal desalination plant of the third South Pars refinery with Mitreh
Benefits of chemical washing:
- Increase efficiency by up to 40%
- Reduce energy consumption and operating costs
- Increase equipment life
- No need for long production line downtime
- Possibility of on-line (while the system is running)
Main Chemical Cleaning Methods
1. Acid Cleaning
- Use:Removal of mineral deposits (calcium carbonate, sulfates, iron oxide)
- Common materials:
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) → Effective on carbonates and metal oxides
- Sulfuric acid (H₃PO₄)→Milder, suitable for more sensitive equipment
- Citric acid → More biocompatible, suitable for the food and pharmaceutical industries
- Advantages:High speed, deep impact on hard deposits
- Disadvantages:
- High safety risks (toxicity, hazardous gases)
- Severe corrosion of metals
- Need for corrosion inhibitor
- Production of heavy and contaminated effluents
- Need for complete system shutdown
Note:The use of strong acids such as 10% HCl in laboratory conditions has shown a weight loss of metal coupons of up to 40% — a sign of severe corrosion.
2. Alkaline Cleaning
- Uses: Removal of grease, oil, organic and protein deposits, biofilms
- Common ingredients: Caustic soda (NaOH), sodium carbonate, phosphates
- Applications: Cooling systems, food industry, water softeners
- Advantages: Safer than acids, suitable for sensitive systems
- Disadvantages: Less effect on mineral deposits
3. Chelant Cleaning
- Uses substances such as EDTA or NTA that form bonds with metal ions and dissolve them.
- Suitable for high-pressure boilers and sensitive equipment.
- Reduces the risk of corrosion from mineral acids.
4. Two-stage washing (Acid-Alkali Sequence)
A combination of alkaline (for grease) and acid (for mineral deposits) washing for systems with mixed contamination.
5. Cold Mitreh Chemical Washing (MDA0102) — A Modern and Safe Method
In recent years, the need for safe, sustainable and non-stop solutions has led to the development of products that perform descaling without the hazards of acids. One of these advanced solutions is the Cold Mitreh Chemical Washing (MDA0102) manufactured by Abrizan.
Key features of cold mitreh:
- Non-acidic and non-corrosive: no risk to metals, personnel and the environment
- Complete descaling: dissolving calcium carbonate, calcium sulfate and iron oxides
- No need to stop the system: can be used on-line
- Formation of a protective layer: reducing future corrosion and preventing the formation of new deposits
- Environmentally friendly: its waste after removing chlorine can be used in green space irrigation
Cold mitreh applications:
System type | Application |
Cooling Tower | Removal of deposits from packing, pipes, nozzles |
Heat exchangers | Increased heat transfer efficiency |
Steam boilers and boilers | Preventing fouling and reducing fuel consumption |
Refrigeration systems | Improving the performance of condensers and evaporators |
Heating packages | Non-destructive cleaning |
Food industry | Food Grade version without risk to health |
Laboratory results (based on study MDA0102):
- In a pilot cooling tower test, cold mitreh completely removed scale.
- Iron and copper coupons remained corrosion-free.
- Water analysis showed a significant increase in dissolved solids—an indication of high solvency power.
- In contrast, 10% hydrochloric acid caused severe corrosion and produced heavy effluent.
Conclusion:Cold mitreh is not only an effective scale remover, it also protects the system and provides long-term stability.
Steps to Perform Chemical Cleaning
Although methods vary, the general steps of chemical cleaning are as follows:
1. Initial inspection and identification of the type of deposit (by XRD analysis or sampling)
2. Design of appropriate chemical formulation
3. Isolate the system (if shutdown is required)
4. Pre-rinse with water or pre-cleaning solution
5. Injection of cleaning solution (e.g. cold mitreh) and contact period
6. Final rinse with deionized or distilled water
7. Post-rinse (Passivation) — creating a protective layer on the metal surface
8. Final inspection and delivery of the system
Note: In cold mitreh cleaning, many steps (such as system shutdown and post-rinse) are not required and the process is performed on-line with minimal intervention.
Detergents widely used in industry
Detergent | Type | Main application | Safety |
Hydrochloric acid | Acidic | Calcium carbonate removal | Low (toxic, corrosive) |
Citric acid | Low acid | Boilers, sensitive systems | Medium |
Caustic soda | Alkaline | Removing fat and oil | Moderate (risk to skin) |
EDTA | Low acid | High pressure systems | Top |
Cold Mitreh (MDA0102) | Non-acidic | All heating and cooling systems | Very high |
Environmental Tip: Cold mill effluent contains minerals that can be absorbed by plants and, after chlorine removal, can be used for irrigation—unlike acidic wastewater that requires complex treatment.
Chemical Washing Applications in Various Industries
Industry | Application |
Oil and gas | Cleaning of pipelines, exchangers, boilers |
Refineries | Washing of distillation towers, condensers |
Power plants | Cleaning of boilers, condensers, cooling systems |
Food industry | CIP (Clean-in-Place) washing without health risks |
Cooling facilities | Increasing chiller efficiency, reducing electricity and gas consumption |
Cooling towers | Preventing clogging of packing and nozzles |
Safety tips in chemical cleaning
Safety is essential in chemical cleaning. Especially when using acids:
- Use of personal protective equipment (PPE) including gloves, goggles, masks and resistant clothing
- Proper ventilation in closed environments
- Accurate labeling of chemicals
- Monitoring pH and concentration of materials during the process
- Compliance with HSE (Health, Safety, Environment) standards
Advantage of cold mitreh:This product is non-toxic, non-corrosive and free of hazardous gases and does not require complex safety equipment.
Comparison of descaling methods
Criteria | Acid washing | Physical methods | Cold Mitreh |
Efficiency | Efficiency | Low (incomplete sedimentation) | Very high |
Safety | Down | Moderate (risk of physical harm) | Very high |
System stop | yes | yes | No (on-line) |
Corrosion | Very high | Medium (tube deformation) | Very low |
Wastewater | Contaminated, needs purification | No waste | Can be used in agriculture |
Total cost | Up (Repairs, Stop) | Medium | Low (long-term savings) |
Economic savings using cold mitreh
Based on real data from industrial units:
- In a 120-ton chiller condenser, after using cold mitreh:
- 25% increase in heat transfer efficiency
- 40% reduction in pressure drop
- Reduction in gas consumption by up to 30%
- Annual cost of descaling with cold mitreh: Very low
- Cost of replacing a condenser: Very high
- Return on investment in less than 3 months
Conclusion:Using cold mitreh not only reduces current costs, but also avoids heavy capital costs (equipment replacement).
Some projects we have completed with descaling solutions:
1. South Pars 8th Refinery (Chemical washing of thermal desalination water with cold desalination solution)
2. South Pars 9th Refinery (Chemical washing of thermal desalination water with cold desalination solution)
3. South Pars 12th Refinery (Chemical washing of thermal desalination water with cold desalination solution)
4. Bandar Imam Petrochemical (Descaling of heat exchangers with desalination solution)
5. Shahid Madhej Power Plant, Ahvaz (Descaling of condenser with desalination solution)
6. Jam Petrochemical (Descaling of plate exchangers with desalination solution)
7. Asaluyeh 3rd Refinery (Descaling of thermal desalination water with desalination solution)
8. Morvarid Petrochemical (Chemical washing of plate exchangers with desalination solution)
9. South Pars 3rd Refinery (Descaling of desalination package with desalination solution)
10. And many other projects of Abrizan...
Conclusion: The future of chemical cleaning is safe and sustainable
Chemical cleaning and descaling is no longer a repair process, but a smart strategy to optimize industrial performance. Given the energy crisis, water shortages and environmental pressures, the need for solutions like Mitreh Cold is felt more than ever.
This product not only removes deposits, but also:
- Protects the system
- Operates without system downtime
- Is safe for personnel and the environment
- Provides long-term economic savings
In industries where production line downtime = loss of revenue, traditional methods such as acid cleaning are no longer up to date. The future belongs to smart, safe and sustainable solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Does Cold Mitreh really work without stopping the system?
Yes. This product can be used on-line and does not require system shutdown.
2. Is Cold Mitreh suitable for the food industry?
Yes. Its Food Grade version is suitable for food and pharmaceutical systems.
3. When should Cold Mitreh be used?
Periodically (every 6 to 12 months) or when a decrease in system efficiency is observed.
4. Can Cold Mitreh waste be disposed of?
After chlorine removal, its waste can be used for green space irrigation.
5. Is Cold Mitreh only for cooling towers?
No. It is suitable for exchangers, boilers, chillers, packages and all heating and cooling systems.
Final conclusion:
Chemical washing with Cold Mitreh (MDA0102) is a combination of technology, safety and sustainability. This solution not only solves today's problems, but also prevents tomorrow's problems.
For free consultation and to order a variety of cold mitreh products, visit our contact page.
share :













Submit your opinion
Your email address will not be published.