Corrosion and anti-corrosion materials

Effect of chlorine ions on stainless steels
The effect of chlorine and chloride parameters on the corrosion of stainless steels and the parameters affecting their corrosion rate, as well as the acceptable limits of chlorine ion levels in water and the differences in the effects of free chlorine and chloride on the corrosion of corrosion-resistant steels, are stated.

Caustic corrosion
Localized corrosion caused by the concentration of caustic or alkaline salts, which usually occurs under conditions of high evaporation or heat transfer. Caustic salt or caustic soda is one of the most widely used ionic compounds and is used in various industries including water treatment, cardboard and paper production, oil and refinery industries, aluminum production industries, food industries, alcohol production and glass.

Corrosion and deposition of cooling water based on API 571
It refers to general or localized corrosion of carbon steels and other metals caused by dissolved salts, gases, organic compounds, or microbiological activity.
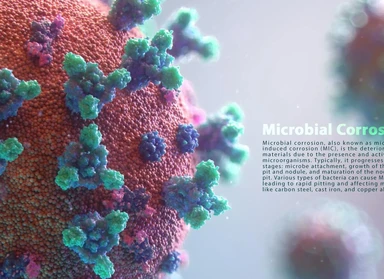
Microbial corrosion based on API 571
Microbial corrosion is a type of corrosion caused by living organisms such as bacteria, algae, or fungi. This type of corrosion is often associated with tubercles or slimy organic materials.

Corrosion process in different environments
Corrosion processes are divided into three groups in a more comprehensive classification: corrosion in aqueous solutions or environments, corrosion in molten salts and liquid metals, and corrosion in gases.

Oil-soluble corrosion inhibitor for the protection of oil transfer and storage equipment
Corrosion is a natural phenomenon that occurs as a result of the electrochemical reaction of metal with the surrounding environment. In the oil and gas industry, corrosion is one of the major problems that accounts for a huge amount of money annually. Part of these amounts are related to the corrosion of pipes or oil transmission lines. Effective ways to prevent corrosion of oil transmission and storage equipment are divided into two categories: physical and chemical solutions.

couponing
The coupon method or corrosion coupons is the simplest method of corrosion monitoring. Coupons are the oldest corrosion monitoring tool. Corrosion coupons are small pieces of metal or alloy of the material of interest that are immersed in the process medium and removed after a specified period of time and their weight or dimension loss is evaluated and examined.

Deaerators
Deaerators are mechanical devices that remove dissolved gases from the boiler feedwater. By reducing the concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the solution, they minimize corrosion and protect the boiler from the effects of corrosive gases.

Anti-corrosion of metals
Anti-corrosion of metals is a very important product that all industries need for the durability of their equipment.

Cooler anti-fouling
Anti-fouling is a protective coating for your air conditioner or cooling device at home or at work. This is a summary of the optimal performance of an anti-fouling coating. The air conditioner tries to produce cool air by evaporating water. The salts left over from the evaporation of water cause problems for the engine and parts of the air conditioner, and the role of the anti-fouling is to protect the air conditioner from the harmful effects of this fluid.

Anti-corrosion Mitreh
How to prevent corrosion and scale in boilers, chillers, and cooling towers? Mitreh's anti-corrosion and anti-scale solution with specialized formulations increases the efficiency and life of equipment.

The role of neutralizers in reducing corrosion
Neutralizers reduce corrosion by reducing the concentration of H+ ions in the solution.

atmospheric-corrosion-inhibition
Some organic compounds with low vapor pressures of about 10-2 to 10-7 mmHg evaporate in a closed space and become liquid on the surface to be protected. These inhibitors increase the corrosion resistance of the metal in corrosive environments. Vapor phase inhibitors are particularly useful for preventing atmospheric corrosion. Atmospheric corrosion results from the single or combined action of moisture, oxygen, and atmospheric pollutants such as SO2, NO2, as well as rain, snow, dust, soot, ash, wind, and radiation.

Uniform corrosion inhibition
Corrosion of metals in acidic environments can be inhibited by a variety of substances. These substances can include simple elements such as chloride, bromide, or iodide ions, or organic compounds, especially those containing elements from groups V and VI of the periodic table such as nitrogen, phosphorus, arsenic, oxygen, sulfur, and selenium in their functional groups.

Local corrosion inhibitor
Localized corrosion occurs on metals that are coated with rutile layers. This can be caused by defects or breakage of the rutile layer. Attacking ions such as chloride cause the rutile layer to break down at weak points on the metal surface. In this case, the bulk of the metal is in a rutile state while small localized areas of it are in an active state.

Corrosion inhibitors and their types
Today, due to the understanding of the metal-electrolyte system, it has become common to prevent corrosion with the help of corrosion inhibitors. Inhibitors are chemicals that, when added in small amounts to a corrosive environment, greatly reduce the rate of corrosion. The composition and types of inhibitors are very diverse. One of the most important ways to classify these materials is based on their mechanism of action and composition.
