Heat exchanger

Warning signs that indicate the need for chemical cleaning of the heat exchanger
Has your heat exchanger lost its efficiency? 5 warning signs (increasing temperature, decreasing ΔT, high pressure, leakage, bad smell) + quick diagnosis checklist.

Determining energy savings and financial return to the employer using Mitreh solution
One of the most important points in a heat exchanger is the overall heat transfer coefficient. This coefficient is obtained in terms of the conduction and convection resistances between the fluids separated by flat walls and cylindrical shells, respectively. The layer of scale on the surfaces may increase the resistance to heat transfer between the two fluids to a large extent. This effect can be taken into account by introducing an additional thermal resistance, called the fouling coefficient (Rf), and its value depends on the operating temperature, fluid velocity, and the operating time of the exchanger.

The anti-fouling and corrosion effect of mitreh in heating and cooling systems
One of the main factors of scale in building installations is the presence of calcium carbonate in water, because the solubility of this compound in water is very low and if the conditions are right, it will precipitate quickly. One of the parts that provides these conditions is the surfaces in contact with water in heat exchangers in domestic gas-fired boilers (heat packages).
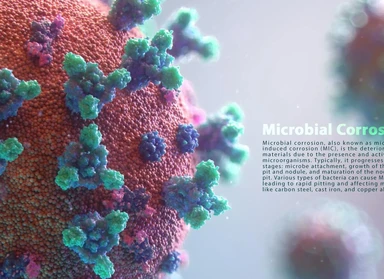
Microbial corrosion based on API 571
Microbial corrosion is a type of corrosion caused by living organisms such as bacteria, algae, or fungi. This type of corrosion is often associated with tubercles or slimy organic materials.

Industrial Mitreh (sediment remover and anti-corrosion)
Any system where temperature and water are the main elements for its operation inevitably requires the invention of Abrizan Company, called Industrial Mitreh, because wherever there is temperature and water, the formation of sediment is inevitable, unless a substance is used that suspends these sediments. This is the main function of an excellent anti-sediment solution.

Power plant cooling system
Thermoelectric power plants boil water to create steam, which then turns turbines to generate electricity. The heat needed to boil the water can come from burning fuel, nuclear reactions, or the sun. As the steam passes through a turbine, it must be cooled back to water before it can be used again to generate more electricity. Colder water cools the steam more effectively, increasing the efficiency of electrical energy generation.

Water management in refineries
Feedwaters to a refinery are usually treated before being used in various processes. The type of treatment depends on the quality of the source water and its end use in the refinery. Turbidity, sediment, and hardness are examples of source water characteristics that may require treatment.

Water vapor and its properties
Comprehensive guide to steam: saturated steam, superheated and flash + steam tables, enthalpy, applications in turbines and industry. Everything about steam from a thermodynamic perspective!

Physical and chemical descaling methods
In industries such as oil, gas and petrochemical, there is always an attempt to prevent the formation of deposits using different methods in equipment such as heat exchangers and boilers. In this field, a lot of money is spent on chemical materials and additives. But most industrial heat exchangers are exposed to sedimentation due to various reasons such as the low quality of water in different areas. These deposits are mostly formed in the pipes of the converters. In order to reduce the losses caused by sedimentation, the converter must be continuously monitored and cleaned.

Sediment formation in boilers
Boiler feed water should be free of hardness. Sometimes, due to the short or improper operation of the hardness device or the failure to regenerate the resins in time, some hardness enters the boiler feed water. Increasing the water temperature in the boiler reduces the solubility of water solutes. The water near the hot surfaces becomes saturated and the conditions for deposition of less soluble substances are provided and eventually sediment is formed.

Cooling tower anti-fouling mitreh
Mitreh cooling tower antifouling is one of the innovative products of Abrizan company. Using an excellent combination, this product serves all industries and huge buildings that use cooling towers to exchange and remove water heat. By preventing the formation of sediment, the mitreh product increases the performance of this system, a system that plays the role of a heat exchanger.

Types of heat exchangers in the industry
There are various types of heat exchangers in the industry, examples of which include: double-tube, plate, spiral tube and shell-and-tube heat exchangers, each of which has its own working method. Also, each heat exchanger has its own advantages and disadvantages.